Raast: Pakistan’s Instant Payment System for a Digital Future
Introduction
Pakistan’s financial sector is undergoing a significant transformation with the launch of Raast Payment Receipt System, the country’s first instant digital payment system introduced by the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) in collaboration with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and Karandaaz. Officially launched in 2021, Raast is part of Pakistan’s National Payment Systems Strategy, aimed at promoting financial inclusion, reducing cash dependency, and digitizing the economy.
What is Raast?
Raast, meaning “direct” or “straight path” in Urdu, is an instant, reliable, and cost-effective payment system that allows individuals, businesses, and government entities to transfer funds quickly and securely.
Key features include:
- Instant fund transfers (real-time processing).
- Low or zero transaction costs.
- Interoperability across all banks, fintechs, and mobile wallets.
- 24/7 availability for users.
- Raast ID (using CNIC, phone number, or email instead of long account numbers).
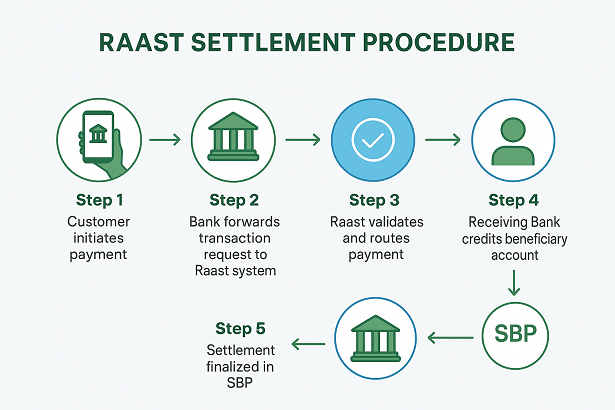
Why Raast Matters for Pakistan
- Financial Inclusion
Pakistan has over 100 million adults without a bank account (World Bank, 2021). Raast provides an affordable digital platform for individuals in rural and underserved areas, making banking more accessible. - Cost Reduction
Traditional banking and money transfer services often carry high fees. Raast transactions are either free or minimal-cost, encouraging wider adoption. - Government Payments
Raast supports government-to-person (G2P) transactions such as salaries, pensions, and social welfare programs (e.g., Ehsaas, BISP), ensuring timely and transparent disbursement. - Business Growth
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) can use Raast for faster, cheaper payments, reducing dependency on cash and increasing efficiency. - Digital Economy Boost
Cash-based economies limit transparency. Raast helps Pakistan transition towards a documented and digital economy, reducing tax evasion and improving governance.
Raast Payment Reeipt System in Daily Life
- A student can receive money from parents instantly via phone number instead of waiting for bank transfers.
- Shopkeepers can accept Raast payments without POS machines.
- Government can directly credit financial aid to recipients without middlemen.
Challenges in Implementation
While Raast Payment Receipt System is a groundbreaking initiative, challenges remain:
- Low digital literacy among rural populations.
- Internet and smartphone penetration gaps (especially in remote areas).
- Trust and security concerns about online transactions.
- Resistance from traditional money transfer operators.
Future Prospects
Raast is being rolled out in phases:
- Person-to-Person (P2P) payments (already live).
- Bulk payments for government and private institutions.
- Merchant payments integration (POS, QR codes, online payments).
Once fully deployed, Raast has the potential to become the backbone of Pakistan’s digital financial ecosystem, fostering growth in e-commerce, fintech innovations, and cashless transactions.
Conclusion
Raast is not just a payment system but a national step toward economic modernization. By making payments faster, cheaper, and more accessible, it bridges the financial gap for millions of unbanked citizens, empowers businesses, and supports government transparency. With continued investment in digital infrastructure and awareness, Raast could be a game-changer for Pakistan’s financial inclusion journey.

